The thyroid, a small, butterfly-shaped gland at the base of your neck, plays a larger role in your health than you might realize. When it functions properly, you probably don’t give it much thought. But when conditions like Hashimoto’s Disease arise, understanding your thyroid becomes crucial. With millions affected globally, Hashimoto’s Disease is one of the most common causes of hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid).
What Is Hashimoto’s Disease and Who Does It Affect?
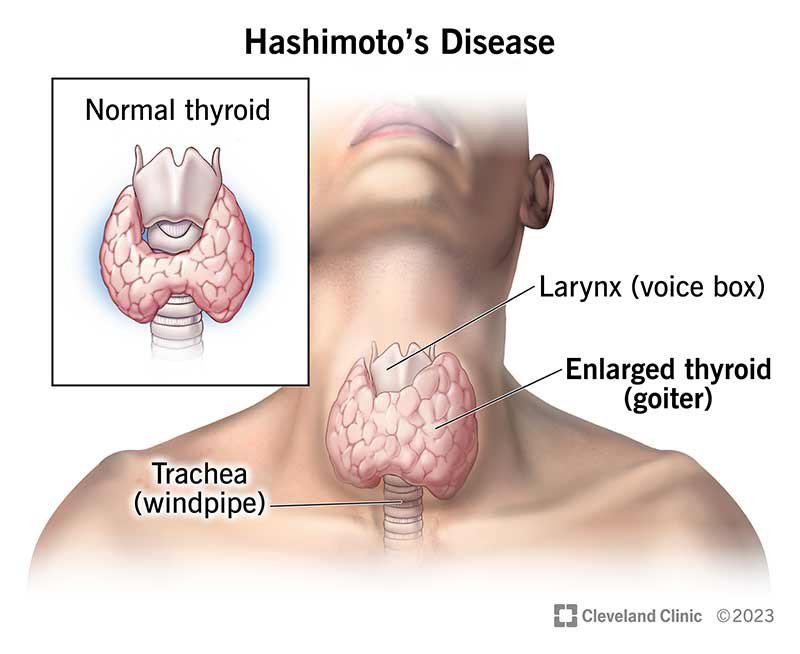
Hashimoto’s Disease, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disorder. This means that the body’s immune system mistakes the thyroid gland for a threat and starts attacking it, causing inflammation and eventually impairing its ability to produce necessary hormones.
The condition is most commonly diagnosed in women, particularly those aged 30 to 50, though men and teenagers can also develop it. If left untreated, Hashimoto’s can lead to complications like goiter (an enlarged thyroid) or severe hypothyroidism, which can significantly impact your overall health.
Understanding the Thyroid and Its Role
To grasp the impact Hashimoto’s can have, it’s important to understand how the thyroid works. This gland produces hormones such as triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which regulate metabolism, energy levels, heart health, and even brain function. Essentially, your thyroid acts as the body’s engine; when it slows down, so does everything else.
When Hashimoto’s leads to hypothyroidism, these essential functions are disrupted. Symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold begin to take root.
Key Symptoms of Hashimoto’s Disease
The tricky thing about Hashimoto’s is that its symptoms often overlap with other conditions, making diagnosis a challenge. The following symptoms may occur gradually and might be subtle at first:
- Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain despite no changes to diet or activity levels.
- Hair Thinning or Loss: Noticeable thinning of the hair, including eyebrows.
- Cold Sensitivity: Feeling unusually cold even when others are comfortable.
- Dry Skin: Increased dryness and itchiness of the skin.
- Constipation: Digestive slowdowns leading to irregular bowel movements.
- Depression or Mood Changes: Feelings of sadness or more severe mood swings.
If you or a loved one experience these signs consistently, it’s important to explore further diagnosis.
Diagnosing Hashimoto’s Disease
Confirming a Hashimoto’s diagnosis requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specific tests. Here’s what to expect during the diagnostic process:
- Blood Tests: These measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). High TSH paired with low thyroid hormones typically indicates hypothyroidism.
- Antibody Tests: Tests that detect thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO antibodies) can signal an autoimmune response.
- Ultrasound: Sometimes, an ultrasound is conducted to examine the thyroid’s size and texture, as an enlarged or inflamed thyroid may indicate Hashimoto’s.
Early detection is paramount as it allows for timely Hashimoto’s thyroiditis treatment, such as those offered in Salt Lake City, preventing further complications.
Treatment Options for Hashimoto’s Disease
Though there is no complete “cure” for Hashimoto’s, effective treatments are available to help manage its symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
1. Medication
The centerpiece of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis treatment is levothyroxine, a synthetic version of the hormone T4. This daily medication replaces the hormones your thyroid can no longer produce on its own. With proper monitoring, most patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms.
2. Dietary Adjustments
While no specific diet can cure Hashimoto’s, certain foods and nutrients support thyroid health:
- Iodine: An essential element for thyroid function, though avoid excess.
- Selenium: Found in Brazil nuts and fish, selenium may reduce thyroid inflammation.
- Gluten-Free Diets: Some patients find symptom relief with gluten-free eating, especially if they have concurrent gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Restoring balance in your life can make a huge difference:
- Stress Management: Stress can worsen autoimmune responses. Consider yoga, meditation, or journaling.
- Regular Exercise: Light to moderate physical activity can help combat fatigue and maintain a healthy weight.
4. Monitor and Adjust
Managing your condition doesn’t stop once you begin treatment. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are vital to monitor hormone levels and make any necessary adjustments.
Living with Hashimoto’s Disease
Receiving a diagnosis of Hashimoto’s Disease can feel overwhelming, but it’s possible to lead a fulfilling, healthy life with the right approach. Here are some actionable tips for managing life with the condition:
- Educate Yourself: Learning about Hashimoto’s helps you understand what’s happening in your body. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
- Build a Support System: Connect with healthcare providers who specialize in thyroid health. Joining support groups—online or in person—can also provide emotional relief and valuable insights.
- Keep a Symptom Journal: Tracking symptoms can reveal patterns or triggers, making it easier to communicate with your doctor.
- Follow a Routine: Establishing consistent eating, sleeping, and medication schedules helps your body adjust and thrive.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Managing a condition like Hashimoto’s is a marathon, not a sprint. Appreciate every improvement in how you feel.
Conclusion
Hashimoto’s Disease may be a lifelong condition, but it can be effectively managed with the right combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and ongoing care. Armed with accurate information and support, you can take control of your thyroid health and live a balanced life.